数据结构(c语言):列表
本章介绍c语言实现的线性表,包括顺序表和链表。
数据结构入门
推荐使用《数据结构》严蔚敏 清华大学出版社 传送门:http://product.dangdang.com/22601051.html。
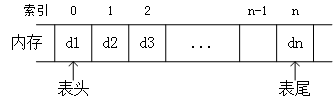
线性表的顺式实现:
#include
#include
#define Size 4
typedef struct SeqList {
int * head;//声明了一个名为head的长度不确定的数组,也叫“动态数组”
int length;//记录当前顺序表的长度
int size;//记录顺序表分配的存储容量
}SeqList;
SeqList initList() {
SeqList t;
t.head = (int*)malloc(Size*sizeof(int));
if (!t.head) {
printf("初始化失败");
exit(0);
}
t.length = 0;
t.size = Size;
return t;
}
SeqList listInsert(SeqList t, int i, int e) {
if (i < 0 || i > t.length) {
printf("插入位置有问题");
return t;
}
if (t.length == t.size) {
t.head = (int) realloc(t.head, (t.size+1)*sizeof(int));//改变head指向的内存空间大小
if (!t.head) {
printf("存储分配失败");
return t;
}
t.size++;
}
for (int j = t.length - 1; j >= i; j--) {//逐个后移
t.head[j + 1] = t.head[j];
}
t.head[i] = e;
t.length++;
return t;
}
SeqList listDelete(SeqList t, int i) {
if (t.length == 0) {
printf("顺序表已空");
return t;
}
else if (i < 0 || i > t.length-1) {
printf("删除位置有问题");
return t;
}
for (int j = i; j < t.length - 1; j++) {//逐个前移
t.head[j] = t.head[j + 1];
}
t.length--;
return t;
}
int listGet(SeqList t, int i) {
if (i < 0 || i > t.length - 1) {
printf("参数非法");
return NULL;
}
else {
return t.head[i];
}
}
int listSize(SeqList t) {
return t.length;
}
void display(SeqList t) {
for (int i = 0; i
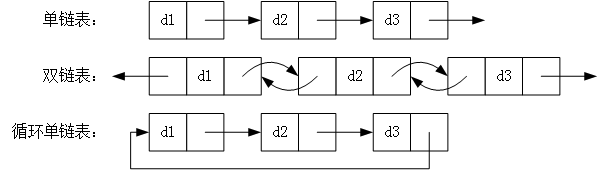
线性表的链式实现:
#include
#include
typedef struct DLNode {
int e;
struct DLNode *pre;
struct DLNode *next;
}DLNode;
DLNode * initLink() {
DLNode *p = (DLNode*)malloc(sizeof(DLNode));//申请头结点
p->pre = p;//构成前驱指针循环链表
p->next = p;//构成后驱指针循环链表
}
DLNode * insertElem(DLNode *p, int i, int e) {
DLNode *m = p;
int j = -1;
while(m->next != NULL && j < i) {
m = m->next;
j++;
}
if (j != i) {
printf("插入位置有问题");
return p;
}
DLNode *n = (DLNode*)malloc(sizeof(DLNode));//创建插入结点n
n->e = e;
n->pre = m->pre;
m->pre->next = n;
n->next = m;
m->pre = n;
return p;
}
DLNode * removeElem(DLNode *p, int i) {
DLNode *m = p;
int j = -1;
while (m->next != NULL && j < i) {
m = m->next;
j++;
}
if (j != i) {
printf("删除位置有问题");
return p;
}
m->pre->next = m->next;
m->next->pre = m->pre;
return p;
}
int getElem(DLNode *p, int i) {
DLNode *m = p;
int j = -1;
while (m->next != NULL && j < i) {
m = m->next;
j++;
}
if (j != i) {
printf("查找位置有问题");
return -1;
}
return m->e;
}
int getSize(DLNode *p) {
DLNode *m = p;
int size = 0;
while (m->next != p) {
m = m->next;
size++;
}
return size;
}
void display(DLNode *p) {
DLNode *m = p;
while (m->next != p) {
m = m->next;
printf("%d", m->e);
}
printf("\n");
}
int main() {
//初始化链表(1,2,3,4)
printf("初始化链表为:\n");
DLNode *p = initLink();
for (int i = 0; i < 5; i++)
{
p = insertElem(p, i, i+1);
}
display(p);
printf("在第5的位置插入元素8:\n");
p = insertElem(p, 4, 8);
display(p);
printf("删除第4个元素:\n");
p = removeElem(p, 3);
display(p);
printf("查找第3个元素:\n");
int ele = getElem(p, 2);
printf("第3个元素为:%d\n", ele);
return 0;
}
双向循环链表的c语言实现:
#include
#include
typedef struct SLNode {
int e;
struct SLNode *next;
}SLNode;
SLNode * initLink() {
SLNode *p = (SLNode*)malloc(sizeof(SLNode));//申请头结点
p->next = NULL;//置结束标志NULL
return p;
}
SLNode * insertElem(SLNode *p, int i, int e) {
SLNode *m = p;
int j = -1;
while (m->next != NULL && j < i-1) {//首先找到第i-1个结点
m = m->next;
j++;
}
if (j != i-1) {
printf("插入位置有问题");
return p;
}
SLNode *n = (SLNode*)malloc(sizeof(SLNode));//创建插入结点n
n->e = e;
n->next = m->next;
m->next = n;
return p;
}
SLNode * removeElem(SLNode *p, int i) {
SLNode *m = p;
int j = -1;
while (m->next != NULL && j < i - 1) {//首先找到第i-1个结点
m = m->next;
j++;
}
if (j != i - 1) {
printf("删除位置有问题");
return p;
}
SLNode *n = m->next;
m->next = m->next->next;
free(n);
return p;
}
int getElem(SLNode *p, int i) {
SLNode *m = p;
int j = -1;
while (m->next != NULL && j < i) {//首先找到第i个结点
m = m->next;
j++;
}
if (j != i) {
printf("查找位置有问题");
return -1;
}
return m->e;
}
int getSize(SLNode *p) {
SLNode *m = p;
int size = 0;
while (m->next != NULL) {
m = m->next;
size++;
}
return size;
}
void display(SLNode *p) {
SLNode *m = p;
while (m->next != NULL) {
m = m->next;
printf("%d", m->e);
}
printf("\n");
}
int main() {
//初始化链表(1,2,3,4)
printf("初始化链表为:\n");
SLNode *p = initLink();
for (int i = 0; i < 5; i++)
{
p = insertElem(p, i, i+1);
}
display(p);
printf("在第5的位置插入元素8:\n");
p = insertElem(p, 4, 8);
display(p);
printf("删除第4个元素:\n");
p = removeElem(p, 3);
display(p);
printf("查找第3个元素:\n");
int ele = getElem(p, 2);
printf("第3个元素为:%d\n", ele);
return 0;
}